Anionic Polyacrylamide (APAM)


Short Description:
Product Name: Anionic Polyacrylymide Powder(APAM)
Molecular Formula: (C3H5NO)n
Molecular Weight: 2--12Million
Ionization Degree: 10--60%
Solid Content: ≥90%
Dissolve Time: ≤60 min
Residual Unit: ≤0.10%
Cas No: 9003-05-8
EINECS No: 231-545-4
HS Code: 3906 9010 00
Package: 25KG Woven Bag or follow buyer's requirement
Certificate: ISO/MSDS/COA
Application: Water treatment
Sample: Available
Craft: Original carrier-free biological enzyme catalysis
Send Email To Us
Product Introduction

Product Information
Polyacrylamide (PAM for short) is a commonly used artificial flocculant. This product has the properties of flocculation,
thickening, shearing, drag reduction, and dispersibility. It is easily soluble in water and easily decomposed when the
temperature exceeds 120°C. The solid is white or slightly yellow powder, and the liquid is colorless and viscous.
Our company has three types, anionic, cationic, and non-ionic polyacrylamide, which can be obtained through chemical modification.
The homopolymer formed by the polymerization of a single acrylamide is non-ionic, and its molecules are not charged.
The copolymer formed by the copolymerization of acrylamide and anionic monomers (such as sodium acrylate) is anionic,
and its molecules are negatively charged. For the same reason, the copolymer generated by acrylamide and cationic
monomers is cationic, and its molecules are positively charged.
The copolymer contains some ionic monomers, which shows some ionic characteristics. We use the percentage of ionicity
to express how much charge is on the polymer molecular chain. The higher the ionicity, the more charge is on the molecular
chain. In this way, the ionicity of non-ionic polyacrylamide is zero. What charge (i.e. ionicity) and how much charge (i.e. ionicity)
the polyacrylamide molecular chain carries are important considerations when selecting polyacrylamide flocculants.
Polyacrylamide is a synthetic polymer with a relatively high molecular weight. The molecular weight of polyacrylamide
always refers to the average molecular weight, which indicates the average length of each polymer molecule.
The larger the molecular weight, the more chain segments each molecule contains, or the longer the average length of each molecule.
From the perspective of molecular weight, the flocculation effect of polyacrylamide is not only related to the molecular weight,
but also to the molecular structure (straight chain, branched chain, cross-linked) and molecular weight distribution (wide, narrow).
Product Name | Cationic Polyacrylamide | Molecular Formula | (C3H5NO)n |
CAS NO | 9003-05-8 | Molecular Weight | 2--12 Million |
| EINECS NO | 231-545-4 | HS Code | 3906 9010 00 |
| Ionization Degree | 10--60% | Solid Content | ≥90% |
| Dissolve Time | ≤ 60 min | Residual Unit | ≤0.10% |
Product Category
The copolymer formed by the copolymerization of acrylamide and anionic monomers (such as sodium acrylate) is anionic polyacrylamide, and its molecules are negatively charged. We use ionicity to represent the charge on the polymer molecular chain. The higher the ionicity, the more charge on the molecular chain.
Anionic polyacrylamide is a high molecular polymer synthesized with a high degree of polymerization. It has high viscosity, large molecular weight, and strong flocculation. There are active groups in the molecules, which can change the interface state, have affinity with many substances, form large floccules, accelerate the sedimentation of particles in the suspension, and have very obvious effects of accelerating solution clarification and promoting filtration.
What charge (i.e. ionicity) and how much charge (i.e. ionicity) the polyacrylamide molecular chain carries are important considerations when choosing polyacrylamide flocculants.
Product No. | Electric Density | Molecular Weight | Remarks |
5500 | Extreme-Low | Middle-Low | |
| 5801 | Very Low | Middle-Low | |
| 7102 | Low | Middle | |
| 7103 | Low | Middle | |
| 7136 | Middle | High | |
| 7186 | Middle | High | |
| L169 | High | Middle-High | |
How to Use
Polyacrylamide flocculants are high molecular weight organic compounds, most of which have molecular weights
of more than several million, and some are even close to 20 million. Therefore, their dissolution methods are very different
from inorganic small molecular iron salt and aluminum salt coagulants.
Generally speaking, the following principles should be followed:
1. Powdered polyacrylamide flocculants cannot be added directly to sewage. Before use, it must be dissolved in water and
its aqueous solution is used to treat sewage.
2. The water used to dissolve powdered polymers should be clean water (such as tap water), not sewage.
Water at room temperature is sufficient, and generally does not need to be heated. When the water temperature is below 5,
the dissolution is very slow. The dissolution speed increases with increasing water temperature, but above 50 will accelerate the
degradation of the polymer and affect the use effect. Generally, tap water is suitable for preparing polymer solutions.
However, strong acid, strong alkali, and high salt water are not suitable for preparation.
3. For the selection of polymer solution concentration, our company recommends 0.1% to 0.3%, that is, add 1 to 3 grams
of polymer powder to 1 liter of water.
The following factors should be considered when selecting the concentration:
If the preparation tank is too small and the daily dosage is large, it is recommended to prepare a slightly higher concentration
(such as 0.3%); When the molecular weight of the polymer is very high, it is recommended to prepare a slightly lower
concentration (such as 0.1%); When the polymer solution is added to the sewage, if the dispersion condition is not good due
to equipment reasons,it is recommended to prepare a slightly lower concentration. If the polymer concentration is too high,
the agitator motor will be overloaded,and the dispersion condition will be poor after entering the sewage,
affecting the use effect.
4. Do not transfer the prepared solution with a centrifugal pump to avoid shear degradation of the polymer caused by the
high-speed rotating blades. The specific method of preparation is as follows: add a certain amount of clean water to the
container (such as a beaker in the laboratory, a preparation tank in the factory), calculate the required amount of powdered
polymer according to the amount of clean water and concentration, and weigh the polymer; turn on the electric stirrer to stir
the clean water into a vortex, and the linear speed at the end of the stirrer blade should not exceed 8 meters/second to
avoid polymer degradation; but it should not be too slow to avoid polymer particles floating on the water surface,
or sinking and agglomerating in the water.
Slowly sprinkle the polymer into the vortex of water until it is all sprinkled. Note that the polymer particles cannot stick to each other
or clump after entering the water. Then stir for a while to fully dissolve the polymer particles, and finally become a uniform, transparent,
viscous solution without visible lumps.
Regarding the stirring time, determine it according to the following method:
A. In summer when the water temperature is high, anionic and cationic polymers need to be stirred for about 1 hour, and non-ionic
polymers need to be stirred for about 2 hours;
B. In winter when the water temperature is low, anionic and cationic polymers need to be stirred for about 1.5 hours, and non-ionic
polymers need to be stirred for about 3 hours;
Also, the higher the preparation concentration, the faster the polymer dissolves. Uneven or insufficient dissolution will affect the use effect.
Details Images
 |  |
Application:
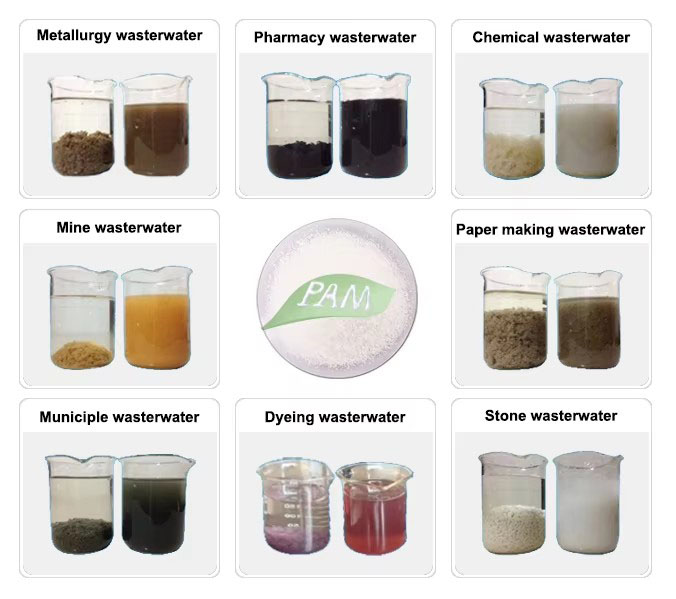

Main uses of anionic polyacrylamide:
1. Industrial wastewater treatment: Especially for suspended particles, coarse, high concentration, particles with positive charge,
neutral or alkaline PH value of water, electroplating, circuit board, papermaking, printing and dyeing, bleaching and dyeing,
leather making and other wastewater treatment, the effect is ideal.
2. Drinking water treatment: The water source of many tap water plants in my country comes from rivers. The sediment and
mineral content is high and relatively turbid. Although it has been precipitated and filtered, it still cannot meet the requirements
and needs to be added with flocculants. In the past, water plants used inorganic flocculants, but the dosage was large,
resulting in an increase in sludge volume and poor effect. Anionic polyacrylamide is used as a flocculant, and the dosage
is 1/50 of that of inorganic flocculants, but the effect is several times or even dozens of times that of inorganic flocculants.
For river water with serious organic pollution, it is better to use it in combination with cationic polyacrylamide.
3. Papermaking additives: The papermaking industry can be used as a clarifier, retention aid, filter aid, and paper dry and
wet strength enhancer for caustic soda.
4. Used as a sugar juice clarifier in the sugar industry. Used as an additive and binder in aquatic feed.
5. Used in coal washing plants and ore dressing plants for rapid sedimentation of materials with particularly
significant effects.
 |  | |
Cationic polyacrylamide (CPAM) is suitable for the treatment of wastewater containing fine suspended matter, organic matter and colloid due to its unique side chain structure and high density charge. | Textile factory/printing and dyeing factory: can be used for dehydration of residual activated sludge from printing and dyeing wastewater.
| |
 |  | |
| Cationic polyacrylamide can effectively flocculate waste pulp, and form a dense structure, large particles of flocculant, so as to make the paper dense and uniform under the condition of not affecting the paper water filtration performance and retention. In addition, cationic polyacrylamide can resist high shear forces, so it will play a good role in retention and filtration over a wide pH range. The dissolution degree of CPAM has a great influence on the coating and aggregation degree of gold nanoparticles on the surface of paper. CPAM with high charge density dissolves faster and can make the coating and aggregation of gold nanoparticles on paper more uniform and stable. | Sludge colloidal particles are usually negatively charged, and the process of interaction with cationic polyacrylamide is the process of colloidal instability. Polymer cationic groups attract negatively charged sludge ions, reduce and neutralize the surface charge of colloidal particles, and compress the colloidal diffusion layer to make the particles condense and destabilize, and with the help of polymer chain bonding bridging effect, flocculation sedimentation is generated. |
Package & Warehouse
 |  |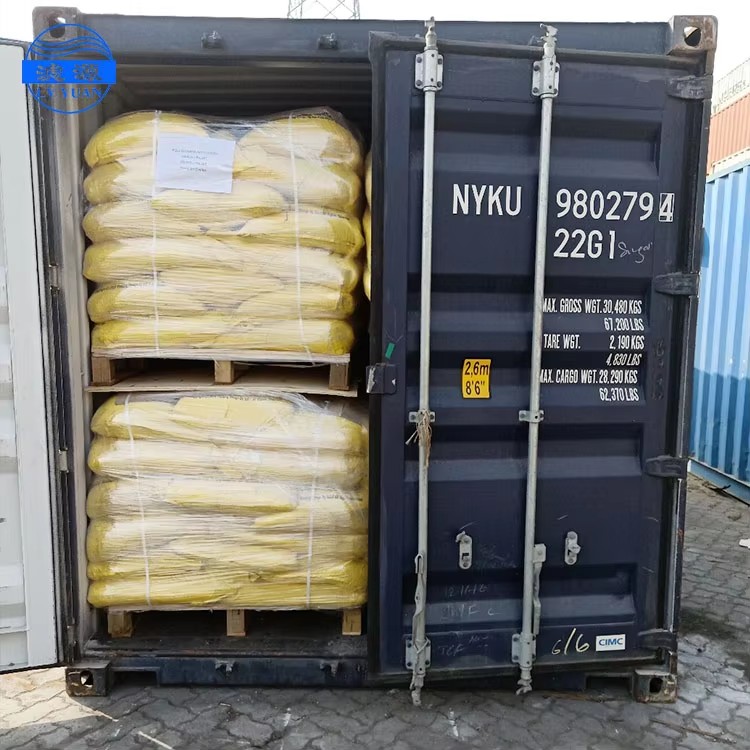  |
Package | 25Kgs / Bag |
Quantity | 14MTS on Pallet /18 MTS without Pallet by 20“ FCL |


 Polyacrylamide dispersant for papermaking
Polyacrylamide dispersant for papermaking Nonionic Polyacrylamide Powder (NPAM)
Nonionic Polyacrylamide Powder (NPAM)